The automobile water pump is a key component of the engine cooling system. Under the action of the axial load, the failure condition of the pump bearing in the bearing hole and the escape is easy to cause serious safety hazard. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze the failure causes of bearing turbulence and to formulate corresponding countermeasures.
Figure 1 shows a typical automobile water pump structure. At one end of the pump bearing, the torque is input through the pulley, and the impeller at the other end is rotated. The centrifugal force is used to deliver the coolant. The fan at the front end of the pulley runs along with the pump, which is the vehicle. The water tank is cooled down. The following is an analysis of the influencing factors of the failure of the car water pump bearing.
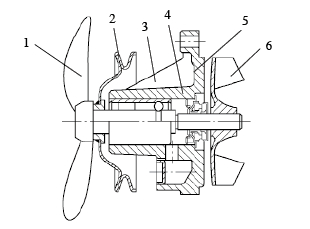
Figure 1 1. Fan 2. Pulley 3. Housing 4. Water pump bearing 5. Water seal 6. Impeller
Effect of temperature change
An interference fit is usually used between the pump bearing and the housing to allow the bearing to withstand certain axial loads. When the temperature of the pump running on the vehicle gradually rises from normal temperature to a higher operating temperature, its components will expand linearly with increasing temperature. When the linear expansion coefficient of the bearing and the housing with a matching relationship is large, the change in temperature will cause a change in the interference, thereby changing the bearing load of the bearing.
Taking a certain type of automobile water pump as an example, the shell material is aluminum alloy ZAlSi9Mg, the bearing material is GCr15, and the design fit size is φ30X7/h6. When the temperature rises from normal temperature 20 °C to 90 °C, the interference is The theoretical calculation of the change is as follows.
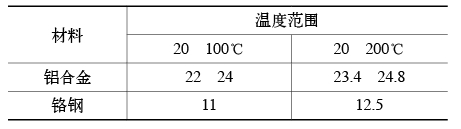
First, according to φ30X7/h6, check the tolerance and the cooperation manual to know the interference is 0.043~0.077mm. Check the material manual for the linear expansion coefficient of the material as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Linear expansion coefficient of material

Then, the amount of expansion of the hole and the shaft is
Δ hole = 30 × 23 × 10 -6 × (90-20) = 0.048 3 (mm)
Δ axis = 30 × 11 × 10 -6 × (90-20) = 0.023 1 (mm)
Reduced interference ΔL=0.048 3-0.023 1=0.025 2(mm)
The reduction ratio of the interference is calculated as follows:
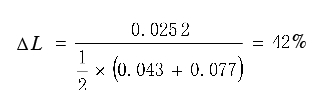
The two sets of pumps were tested for bearing pull-out loads at 20 ° C and 90 ° C to form a comparison curve (see Figure 2). The test data analysis shows that the average out-load of the bearing at room temperature is 10.7kN, and the average out-load of the bearing at 90°C is only 5.9kN. After the temperature rises, the axial load capacity of the pump is reduced by 45%.
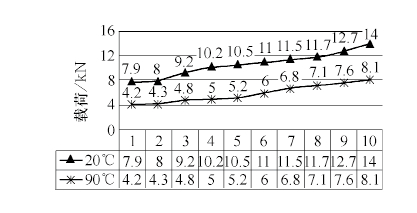
Figure 2 test load comparison curve
Through theoretical analysis and experimental tests, the change in temperature has a great influence on the axial load carrying capacity of the bearing. Therefore, the design of the automobile water pump should fully consider the linear expansion coefficient of the material and the working temperature of the product. If necessary, materials with a small difference in linear expansion coefficient or auxiliary processing methods such as elastic retaining rings can be used to prevent the bearing from escaping.
Influence of machining accuracy of the housing
The main factors affecting the machining accuracy of the bearing bore include the surface roughness and cylindricity. The surface of the bearing bore of the machine tool inevitably has a small spacing and a small peak-to-valley surface, ie surface roughness (see Figure 3), which affects the stability of the pump bearing interference fit. Due to the influence of surface roughness, the effective contact area between the mating surfaces is reduced, and the microscopic peaks are squeezed during assembly, so that the actual effective interference is reduced, and the joint strength is lowered.
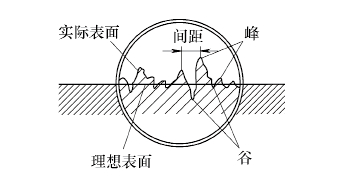
image 3
The cylindricity error includes the error of the axial section and the cross section. The cylindricity error generated in the machining of the bearing shell of the pump casing can also reduce the effective contact area between the mating surfaces, making the bearing connection of the interference assembly unreliable. .
Therefore, the bearing bearing hole machining accuracy should be paid attention to the bearing release load. During the processing of the pump casing, while considering the economy, the surface roughness value and the cylindricity error of the bearing hole should be reduced as much as possible to ensure the joint strength between the bearing and the casing and prevent the bearing from escaping.
Effect of fan operation
When the fan at the front end of the pump rotates, the axial force generated by the air flow and the lateral vibration caused by the excessive imbalance of the fan will affect the reliability of the bearing and become the cause of the failure of the bearing.
According to Newton's third law, the direction of the force of the fan after starting is opposite to the direction of blowing. Tests have shown that when the wind speed of the fan is 7?12m/s, the axial force it receives can reach 5000 8000N, and the direction of the force is back to the fan.
In addition, due to the manufacture and installation of the rotating fan, the actual rotational moment center and its theoretical axis must be deviated, which causes periodic vibration under the action of centrifugal force during the operation of the fan. Expression formula by centrifugal force
F = mrω 2 =mr(2πn) 2
It can be seen that the vibration intensity during fan operation is related to the unbalance amount and the rotation speed. Vibration is very sensitive to bearing damage, and peeling, cracking and wear are all reflected in the bearing vibration. Under the cyclic vibration load of a certain intensity of the pump bearing, the fatigue failure of the joint will occur, causing the bearing to move out, and the direction of the bearing swaying is directed to the fan.
Therefore, the design of the automotive water pump should evaluate and measure the axial force generated when the fan is running, and if necessary, set the thrust device to the bearing. In view of the vibration effect caused by the unbalanced amount, the mass distribution of the fan should be designed to reduce the vibration of the journal or the force acting on the bearing to a specified range during operation; the position of the unbalance generated by the fan is determined during manufacture and Size and eliminate it.
Impeller operation
When the impeller rotates to do work, the fluid medium on the front and rear sides will generate a pressure difference, which will generate axial force, which will affect the bearing's turbulence, especially the impact of high-powered trucks.
Taking a heavy-duty truck water pump as an example, its speed is n=3500r/min, the impeller diameter is d=122mm, and the outlet width is B=13.5mm. The impeller fluid analysis results are shown in Fig. 4.
When the impeller rotates at a high speed, the liquid medium is pulled out to the periphery under the action of the centrifugal force. At this time, a negative pressure zone is formed on the water inlet side of the blade, the pressure is about -106 kPa, and the pressure of the blade back is usually 100 kPa.

Figure 4
F = ΔPS = (P1 - P2) 1/4πD 2
Considering the correction factor, the axial force generated by the impeller can be calculated to be 842N.
It can be seen that the axial force generated by the impeller when the pump is running cannot be ignored, and its direction is the blade facing away from the impeller, which has a great influence on the bearing turbulence. Because the axial force generated by the impeller cannot be eliminated, the axial load of the impeller should be fully evaluated during product design. If necessary, it should be considered to provide a retaining ring or step on the bearing end surface to prevent the bearing from swaying. In the design of the pump, if the blade direction of the impeller is directed toward the fan at the front end of the pulley, the axial force generated by both the impeller and the fan can be partially offset. Thereby reducing the axial load of the water pump bearing, not only can prevent the bearing from escaping, but also can improve the working condition of the bearing and improve the life of the pump.
Impact of installation conditions
Due to the design, manufacture and installation errors of the pump pulley, the center plane and the center plane of the adjacent train wheel cannot be completely overlapped. Therefore, there is an inclination angle α between the V-belt tension direction and the pulley center plane, and the figure 5 is established. The triangle of the force.
The axial static tension of the pump bearing is
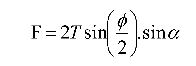
Where T is the pre-tightening force, φ is the wrap angle of the pulley, and α is the dip angle.
Assume that the pump has a preload force T=500N, the belt wrap angle φ=180°, and the belt inclination angle α=4°, then the axial static tension is calculated as follows:
F = 2 × 500 × sin (180 ° / 2) × sin4 ° ≈ 70N
The above calculation does not consider the radial impact load of the belt drive. Due to the presence of the angle of inclination, the bearing is bound to receive a high frequency axial impact load when the pump is running. It is estimated that the bearing is actually subjected to an axial dynamic load of 300 to 500 N. Under the influence of the above factors, the long-running water pump bearing is prone to fatigue failure of the connection, and finally the bearing is detached.
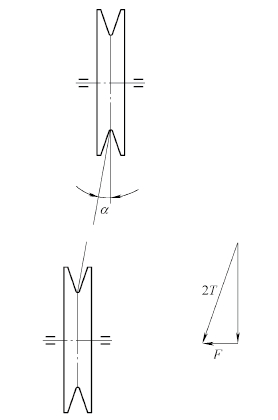
Figure 5
After the pump is installed, the axial deviation of the pulley in the engine train, the parallelism error between the pump rotating shaft and the rotating shaft of the adjacent wheel train, and the vibration of the surrounding components will affect the reliability of the bearing connection and make the bearing appear. Fatigue failure of the joint. Therefore, starting from the design and through the process control to minimize the tilt angle α value of the pump pulley, the axial dynamic load of the water pump bearing can be effectively reduced, and the bearing can be prevented from being pulled out. In addition, increasing the rigidity of the transmission system where the pump is located, reducing the number of vibration sources and their intensity can make the pump run more smoothly and reduce the probability of product failure.
Conclusion
The above factors are analyzed for the influencing factors of the turbulent failure of automotive water pump bearings. The failure is often the result of a combination of various factors. Therefore, in the design and manufacturing process of the product, it is necessary to avoid or eliminate adverse factors, and take necessary precautions to improve the reliability of the water pump and prevent the pump bearing from moving out.
Aromatic Alcohol
In organic chemistry, the aromatic alcohols or aryl-alcohols are a class of chemical compounds
We provide:Terpineol,a-Terpineol,Terpinene-4-ol,Citronellol,Geraniol,Tetrahydrolinalool,Benzene Alcohol,Benzyl Alcohol,PMD,leaf alcohol,Cis-3-hexen-1-ol
Please contact us for more details.
Alcohol
Benzene Alcohol,Benzyl Alcohol,Natural Leaf Alcohol,Natural Terpene Alcohol
Jiangxi Global Natural Spice Co., Ltd. , https://www.chessentialoil.com