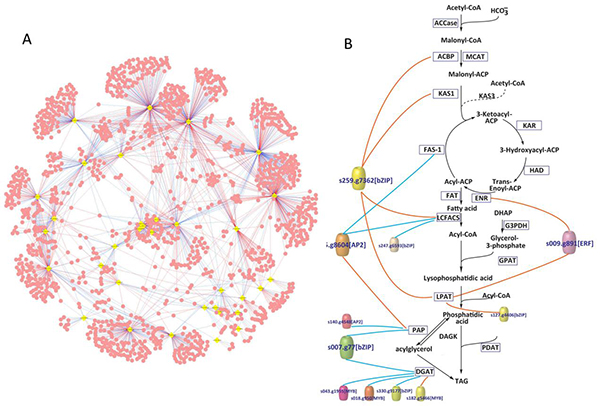
Fig. 1 (A) Calculation method predicts the whole genome transcriptional regulatory network of Nannochloropsis, yellow dots represent transcription factors, and red dots represent target genes. (B) The transcriptional regulatory network of the triglyceride (TAG) synthesis pathway, colored cylinders represent transcription factors, the red line represents positive regulation, and the blue line represents negative regulation.
Some of the microalgae in nature are considered as potential new energy crops due to their high oil production, rapid growth, and strong environmental adaptability. They can be cultivated on marginal lands using seawater or wastewater. However, one of the key bottlenecks in current germplasm selection is the lack of understanding of the mechanism of oil production and regulation of microalgae. Recently, the Single Cell Research Center of the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, uses Micrococcus as a model organism to reveal the first genome-wide transcription factor regulatory network of oil-producing microalgae. Related results were published online in Scientific Reports on June 26th.
Nannochloropsis spp. is a high-yielding oleagin that is widely distributed in the ocean and can be cultivated on a large scale in all parts of the world. The experimental data was based on the experimental data of the six Nannochloropsis genomes (Wang, et al, PLoS Genetics, 2014) and the time sequence transcriptome of oil production (Li, et al, Plant Cell, 2014) collected in the early stage of the project group. Hu Jianqiang, a postgraduate at the Single Cell Research Center of the Energy Institute, systematically explored all transcription factors and their genome binding sites encoded by the genome of Nannochloropsis oceanica through the use and improvement of strategies such as Phylogenetic Footprinting. A transcriptional regulatory network composed of 34 transcription factors, 30 transcription factor binding motifs, and 950 target genes was constructed (Fig. 1A).
Based on the co-expression analysis of transcripts during oil production, the researchers deduced that 11 transcription factors are related to oil production and proposed a transcription factor regulation mechanism for the lipid synthesis pathway (Figure 1B). Relevant information is also displayed through interactive online databases, etc. to efficiently serve domestic and overseas microalgae oil production research groups. In addition, through the comparative analysis of 36 plant genomes including Nannochloropsis, the researchers also found that the composition of the transcription factor family has a close relationship with the occurrence of species germlines. It is believed that the evolution of the transcription factor family may be a single one. One of the important driving forces for the evolution of cell plants to multicellular plants.
The transcription factor regulatory network will provide systematic and abundant clues for the in-depth study of specific transcription factors and their target genes, thus laying the foundation for the development of oil microalgae germplasm selection based on transformation control approaches such as “transcription factor engineeringâ€. At the same time, this study is also of great significance for studying the evolution and origin of plant transcriptional regulatory networks.
The study was supported by the "973" project of synthetic biology and was co-chaired by Xu Jian and Ning Kang.
String Pouch,String Canvas Pouch,String Pouch Bag,String Dust-Proof Pouch
Dongguan C.Y. RedApple Industrial Limited , https://www.hpgbags.com