Abstract: The use of flux cored wire submerged arc surfacing hard surface technology can repair large hot rolling support rolls. This paper describes in detail the characteristics of surfacing welding technology for the manufacture of such rolls, the selection of surfacing materials, and the characteristics and processes of the surfacing repair manufacturing process.
Key words: flux cored wire, large hot rolling support roll, surfacing repair manufacturing
Foreword
As we all know, with the development of modern hot-rolled strip mills in the direction of large-scale, high-speed, and automation, the requirements for hot-rolled support rolls are becoming higher and higher. For large-size support rolls used in hot-rolled strip mills, the following characteristics of rolling should be met [1]:
(1) It has high compressive strength and good rigidity enough to withstand high rolling force and peak load;
(2) Good toughness to avoid breakage of the broken roll, roll body and surface peeling;
(3) The working layer of the roller body has good wear resistance and fatigue resistance to reduce the roller consumption;
(4) The working layer of the roll body has uniform structure and hardness, so that the full roll surface has uniform wear resistance;
(5) It has good corrosion resistance to resist high temperature during hot rolling and corrosion of lubricating or cooling medium.
Based on the above characteristics, the fracture toughness of the alloy forged steel support roll is superior to that of the cast steel support roll because the surface hardness of the alloy forged steel support roll body can reach about 70HSD, and has good wear resistance and high mechanical properties. Therefore, the alloy forged steel support roller has become the main choice for the current hot-rolled strip mill support roller.
Hot-rolled strip mills with large hot-rolled support rolls mainly include: wide-band steel hot strip mill, thin slab (continuous casting) continuous rolling mill, plate mill, wide plate mill, etc., and hot-rolled support rolls are produced on various production lines. One of the important spare parts, each large rolling mill consumes a large number of such rolls every year. Due to the large consumption, the rolls are expensive and more and more attention is paid to the technicians. The quality of the roll not only directly affects its service life, but also has a great impact on the quality, productivity and production cost of the steel. The composite roll repaired by the surfacing method not only has low repair cost, but also can improve the service life of the roll, reduce the roll consumption, rationally use and save the alloying elements, and at the same time improve the efficiency of the rolling mill and the quality of the product, and is effective. Technical and economic measures. Therefore, it is very important to repair the surfacing of the hot-rolled strip mill support rolls to further improve their performance and service life [2~3].
1 surfacing technical requirements
For large hot-rolled backup rolls, the general technical requirements for overlay welding are:
(1) The surfacing layer shall meet the requirements of specific chemical compositions;
(2) The surfacing layer shall have suitable metallographic structure (including matrix structure and carbide);
(3) The surfacing layer should have high anti-flaking performance, good wear resistance and fatigue resistance;
(4) The surfacing layer should have sufficient thickness (up to 70~80mm);
(5) The surfacing layer should have good processability;
(6) In the continuous submerged arc surfacing operation, the welding material has excellent process performance, and the welding slag has good slag removal property (refers to non-stick slag and automatic slag removal);
(7) It has high (surfacing) production efficiency and requires multiple weld repairs after use;
(8) The hardness and hardness uniformity of the surfacing layer after heat treatment meet the technical requirements of the support roller;
(9) There shall be no welding defects such as cracks, pores and slag inclusions in the surfacing layer.
(10) The large supporting roller after surfacing repair shall have a service life not lower than that of the original roller.
2 Surfacing equipment and auxiliary equipment
Due to the large amount of large-scale hot-rolled support roll surfacing repair, 4~7 tons of welding wire can be surfacing once, and continuous surfacing time is long. This puts high performance requirements on the surfacing equipment and corresponding equipment. Surfacing repair large hot-rolled support rolls, special equipment for surfacing and auxiliary equipment should have the following equipment capacity requirements:
2.1 Requirements for special equipment for large-scale roll surfacing (1) The workpiece rotation and support system ensure that the support roller realizes stable and uniform rotation motion without axial movement, and the rotation speed should be continuously adjustable steplessly;
(2) Simultaneous welding of single-wire multi-heads (conditions permit, at least 4 heads), the axial movement of each head should be controlled separately, and it is synchronous, stable and reliable during the surfacing operation. The movement of the machine head adopts AC frequency conversion speed regulation, and the speed regulation range satisfies the requirements of continuous spiral parameters of the surfacing welding support roller;
(3) The vertical lifting of the machine head, the adjustment process shall be smooth, and the lifting height range shall meet the parameters of the surfacing welding support roller;
(4) Due to the long time of continuous surfacing, it is required that all parts of the entire surfacing system be stable and reliable without any failure.
2.2 Large-scale roll surfacing auxiliary device requirements The auxiliary system must have an electric heating (or gas heating) insulation cover device with automatic temperature measurement and temperature control system, in order to ensure the inter-layer temperature technical requirements during the support roller surfacing operation. This is especially important for surfacing repair of large support rolls. In addition, in order to meet the needs of long-term continuous submerged arc surfacing operations, the flux automatic feeding device must also be equipped.
3 surfacing repair process
3.1 Selection of surfacing materials 3.1.1 Selection of welding wire For the different materials (50CrMo, 70Cr3Mo, 3%CrMoV) of large hot-rolled support rolls and the characteristics of rolling, martensitic stainless steel or wear resistance and toughness can be selected. Surfacing welding repair of flux-cored wire material for submerged arc surfacing of Cr-Mo-V (or Cr-Mo-WV-Nb) low-carbon hot tool steel with good thermal stability. The following table shows the recommended alloy composition of surfacing wire materials (reference).
Table Surfacing material alloy composition range (mass fraction, %)

Due to the high carbon content or alloy content of the large hot-rolled support roll base material, in order to ensure a good metallurgical bond between the base metal and the weld overlay metal, that is, to ensure the good combination of strength and toughness of the two, it is recommended to be in the working layer. Before the material is surfacing, the low-carbon compressive strength of the wire material is used for the transition layer surfacing. In order to further reduce the embrittlement of the interface between the base metal and the surfacing layer to avoid local spalling during the use of the support roller, the surfacing of the underlying material may be performed before the surfacing of the transition layer material.
In order to meet the rolling characteristics requirements of large hot-rolled support rolls and the requirements of surfacing technology, the metal matrix structure of the working layer of the roll body is designed as a single low-carbon tempered martensite with high strength and relatively good toughness, and distributed on the substrate. Uniform fine dispersion alloy carbide.
Due to the local peeling of the roll surface which occurs during the use of the original roll, the micro-fracture analysis is mostly caused by sheet-like or strip-shaped non-metallic inclusions. Therefore, it is emphasized here that the purity of the wire material should be Higher requirements are to minimize the content of S, P, H and harmful non-metallic inclusions (sulfides, silicates, oxides, etc.). The wire specification is: Φ4.0mm or Φ5.0mm.
3.1.2 Flux The alkaline sintered flux specially developed and produced by domestically produced is selected. The slag system of the alkaline sintered flux is: MgO-Al2O3-CaF2-SiO2, the basicity BIIW is about 1.8, and the chemical activity coefficient Af is 0.15.
Reason for selection:
(1) Increasing the alkalinity of the flux can reduce the oxygen content and sulfur content of the weld metal and improve its toughness and crack resistance;
(2) In order to solve the problem of high temperature slag removal, the chemical activity of the flux (chemical activity coefficient Af ≈ 0.46 of the smelting flux HJ260) should be reduced and deoxidation should be strengthened.
The application practice shows that the selected domestic alkaline sintering flux has better process performance than HJ260, HJ108, SJ301 and other fluxes, especially with excellent high temperature slag removal performance, which can fully meet the surfacing requirements of large hot rolling support rolls.
3.2 Surfacing repair process plan The following process flow is used to repair the large hot rolling support rolls:
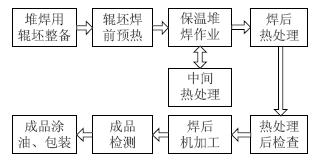
Figure 1 Flow chart of repair process for large hot rolling support roll surfacing
3.2.1 Roller blanking for surfacing Before the repair of surfacing, the old roller blanks are subjected to fatigue layer turning, ultrasonic and magnetic powder (or infiltration) flaw detection, partial defect welding repair, and ensuring the thickness of the surfacing welding layer.
(1) Roll neck flaw detection Before the roll surface processing, the roll neck is subjected to ultrasonic and penetrant inspection. If serious defects are found (especially in the roll body and roll neck transition zone), the subsequent processing of the roll is terminated.
(2) Roller turning process The roll surface fatigue layer is completely removed and turned to ensure the thickness of the weld overlay layer.
(3) Local defect welding repair For local defects, first ensure that the defects are completely removed. Where the turning is deep, the bottoming and transition layer welding materials can be used for welding to make it smooth.
(4) Roller surface inspection The surface of the machined roll is tested to check whether the fatigue layer is turned and the roll body is cracked. If there are still defects, it is necessary to continue turning and eliminate hidden dangers. If the ultrasonic flaw detection of the roller blank has serious internal injuries, it is not allowed to carry out the surfacing repair work of the roller blank.
3.2.2 Preparation before welding Before the roll blank is preheated, the retaining ring should be installed at both ends of the roll body. The retaining ring is welded (disposable), made of thin steel plate (thickness ≥ 6mm), and welded to the opposite ends of the roller body. The function of the retaining ring is to hold the flux to prevent slag from flowing during the overlay welding, thereby ensuring a good weld overlay shape at both ends of the roll.
3.2.3 The main purpose of preheating preheating is to reduce the cooling rate of the surfacing metal and heat affected zone during the surfacing process, reduce the tendency of hardening and reduce the welding stress, and prevent the phase of the base metal and the surfacing metal from occurring during the surfacing process. The change causes cracks to occur. The preheating temperature is determined according to the carbon content and alloy content of the base metal and the surfacing material. Refer to the empirical formula:
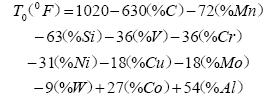
Among them, the preheating and inter-layer temperature should be controlled above the Ms point during the surfacing process to avoid martensite transformation and quenching and tempering effect of the surfacing metal, so that the whole surfacing layer is welded in the heat treatment electric furnace at the same time. The transformation of the body is the only way to ensure the uniformity of the microstructure and hardness of the weld overlay. Due to the relatively high alloy content of the large hot-rolled support roll base material and the surfacing material, the size of the support roll and the thickness of the overlay weld are both large and the welding stress is large, so the preheating and the interlayer temperature should be increased as much as possible. Taking into account the degree of practical tolerance, the preheating temperature is determined to be 400 to 450 ° C, and the inter-layer temperature of the bead is controlled above 350 ° C. During the preheating process, the preheating heating rate is ≤25°C/h; the preheating holding time is determined according to the outer diameter of the support roller (the principle is to ensure the heat penetration of the roller blank from the outside to the inside).
3.2.4 Insulation welding operation
(1) Before welding, the welding wire and the sintered flux are separately baked according to the requirements to remove water.
(2) Using a DC power supply with reduced power supply characteristics, equipped with an electric heating (or gas heating) heat shield device with automatic temperature measurement and temperature control system, and an automatic flux feeding device, on a special equipment for automatic submerged arc surfacing of large rolls , continuous spiral automatic submerged arc welding of multi-head monofilament in the circumferential direction.
(3) The surfacing process must be continuously applied and not allowed to stop in the middle. In case of accidental stop welding, when the interlayer temperature heat preservation device can not guarantee the temperature between the support roller layers, it should be kept into the furnace as soon as possible according to the preheating temperature requirement.
(4) In the circumferential spiral surfacing, in order to prevent the phenomenon of “lack of meat†at the two ends of the roller body, the two ends of the roller body, that is, the first welding part and the final welding part, should be welded in the circumferential direction first. One week (ie, one week of surfacing without moving the welder head), then spiral surfacing. At the same time, in order to ensure the uniformity of hardness between the surfacing layers, it is required that the position of the bead between the surfacing layers be offset by 1/2 of the bead width.
(5) For Φ4.0mm flux cored wire, requirements:
Welding current: 400~450A
Welding voltage: 27~32V
Welding speed: 400~500mm/min (refers to the rotational circumferential speed of the roll surfacing layer)
Weld bead lap joint: The adjacent weld bead overlap must be greater than 50%. The specific lap joint should be smooth and smooth according to the weld bead.
Welding polarity: DC reverse connection.
Power supply characteristics: The falling characteristic with arc voltage feedback is used.
Welding arc lead distance: depends on the roll diameter. Generally, it is in the range of 12.7~50.8mm, and the specific guiding distance is the forming condition of the weld bead.
Wire extension length: 25~35mm
Weld zone temperature: 350~400°C
3.2.5 Intermediate stress-relieving heat treatment Due to the large thickness of the large-scale hot-rolled support rolls (up to 70~80mm), if a continuous surfacing is completed, the surfacing metal will produce very large welding cumulative stress (although always Maintaining at a higher preheating and interlayer temperature), the presence of this cumulative stress will greatly increase the tendency of the surfacing roll to crack, and in severe cases a serious accident of the support roll cracking will occur. Therefore, when the thickness of the weld overlay reaches a certain range, an intermediate stress relief heat treatment is required to reduce or eliminate the cumulative stress of the weld. A prudent measure is to perform an intermediate stress relief heat treatment after surfacing for 20 to 30 mm. The stress-relieving heat treatment temperature is required to be controlled at 480 to 500 ° C, and the time is determined by the thickness of the weld overlay.
3.2.6 Post-weld heat treatment The main purpose of post-weld heat treatment is to improve post-weld microstructure and eliminate weld stress. The post-weld heat treatment of the surfacing repair support roller should be carried out in a special heat treatment electric furnace, which requires good temperature uniformity in the furnace, accurate temperature measurement and precise temperature control process.
After the surfacing support roller is completed, the heat treatment electric furnace should be hoisted immediately for tempering. During the feeding process, the thick steel asbestos pad can be used to prevent the roll temperature from falling rapidly. At the same time, the furnace cannot be cooled, and the initial temperature should be at the preheating temperature of the support roller or Within the inter-layer temperature requirements. During the heating process, in order to ensure uniform temperature, the heating rate should be slow; during the cooling process, in order to prevent new stress, it should be slowly cooled. In order to give full play to the performance of the material, 550~565 °C is selected for medium-high temperature tempering to produce sufficient dispersion strengthening effect. After tempering, the support roller is gradually cooled to 50 ° C before it can be discharged, and it is required to naturally cool to room temperature in still air. The heat treatment process curve is shown in Figure 2:
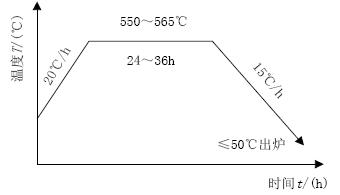
Figure 2 Post-weld heat treatment process curve
3.2.7 Post-heat treatment inspection, machining and finished product inspection The surfacing welding support rolls after post-weld tempering heat treatment are roughed and then semi-finished, including: ultrasonic inspection, hardness inspection, visual inspection, geometry and roughing. Size inspection, etc. The coloring flaw detection (PT) or magnetic particle inspection (MT) inspection of the surfacing layer is performed after the final machining of the support rolls is completed.
3.3 Manual repair welding process for surfacing defects For the submerged arc automatic surfacing method, local micro-defects such as lack of meat, undercut, slag, pores, cracks, etc. in the surfacing layer can be used for manual arcing. The welding method is repaired and repaired. The repair process is as follows:
(1) Before the welding, the grinding wheel should be used to remove the defects and perform the coloring inspection. After confirming that the defect has been completely removed, the repair can be started.
(2) Local preheating with gas or oxygen-acetylene flame, to ensure that the preheating temperature of ≥300 °C is reached within 50 mm around the defect.
(3) The electrode of the surfacing electrode is the same or close to the chemical composition of the surfacing layer, and the diameter is Φ3.2mm. Bake for 1hr at 300~350°C before use.
(4) Use a small welding current, usually 90~110A, with DC power supply, and the welding rod is connected to the positive pole. In order to prevent weld cracks, a method of hot hammering the weld is used. The repair welding repair can be carried out after the post-weld heat treatment, and the heat treatment can be omitted after the repair welding.
4 Surfacing repair quality inspection of hot rolling support rolls
In the process of repair welding of the support rolls, strict inspections shall be carried out in accordance with the contents specified in the “Quality Inspection Essentials†prepared in advance to ensure that the surfacing repair rolls have acceptable chemical composition, mechanical properties and special requirements. Dimensions meet the requirements of roughing drawings, metallographic structure, hardness, ultrasonic flaw detection (UT), magnetic particle inspection (MT) or penetration testing (PT). The quality inspection items in the surfacing repair process should mainly include:
(1) Pre-weld roll blank inspection For the support roll blank to be repaired by surfacing, check the data of the certificate and perform the quality (UT, MT or PT) of the roll neck (especially the roll body part) and Dimensions (guaranteed thickness of the weld overlay) are checked.
(2) Temperature check The preheating temperature check is carried out according to the roll blank preheating specification specified in the "Quality Inspection Essentials". The contact surface thermometer is used to measure the interlayer temperature of the workpiece during the surfacing process. The measuring part is selected at both ends and the center of the roll body, and the interlayer temperature is 20 to 50 ° C lower than the preheating temperature, and this temperature is maintained during the surfacing process.
(3) Surfacing process parameter inspection During the surfacing process, the welding current, arc voltage, welding speed, head moving speed, welding arc guiding distance, weld bead forming and size should be checked at any time, and filled in the record sheet. Inside.
(4) Appearance quality inspection During the surfacing process, the appearance quality of the surfacing layer should be checked at any time, including bead molding, with or without cracks, pores, slag inclusions, undercuts, etc. If defects occur, they should be disposed of in time.
(5) Post-weld inspection After the welding, macro inspection, dimensional inspection and surfacing quality inspection are carried out. After confirming that there are no surfacing defects and the surfacing layer has sufficient machining allowance, the post-weld heat treatment can be performed. After the heat treatment is completed, the roll surface is turned (to leave the remaining grinding allowance), and then the surface hardness inspection, final dimensional inspection, visual inspection, and ultrasonic inspection (UT) inspection (including re-detection of the roll neck). The penetration test (PT) or magnetic particle inspection (MT) inspection of the surfacing layer is performed after the final machining of the support roll is completed.
Spiral Welded Steel Pipe,Black Anneal Tube,Spiral Welded Pipes,Welded Steel Pipe
Steel Tubing,Stainless Pipe Co., Ltd. , http://www.czsteelpipes.com